Imagine a vast interconnected web of information, pulsating with data and communication signals, spanning continents and oceans. This intricate network is not just a virtual entity existing in the digital realm, but a tangible system made up of physical components that enable its existence. The physical components of computer networks are the unsung heroes that work tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure seamless connectivity and efficient data transfer. From cables snaking through buildings to routers humming quietly in server rooms, these components form the backbone of our modern communication infrastructure.
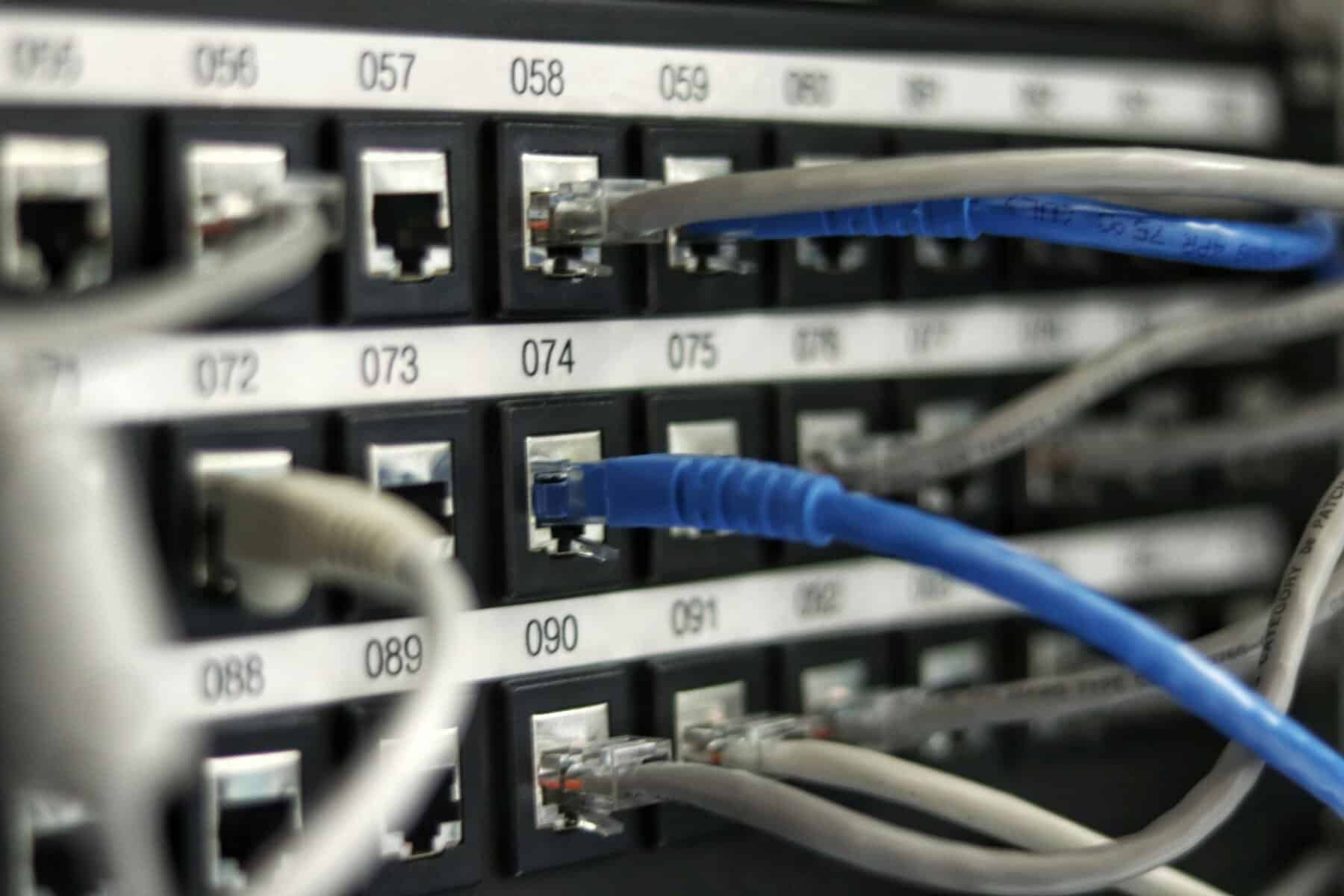


Cables and connectors play a crucial role in the functioning of computer networks, acting as the lifelines that transmit data from one point to another. The type of cable used can significantly impact the speed and efficiency of data transmission, with options ranging from traditional copper cables to modern fiber optic cables. Furthermore, the connectors used to join these cables must be carefully chosen to ensure seamless connectivity and minimal signal loss.
Advancements in technology have led to the development of faster and more reliable cables and connectors, allowing for improved network performance and reduced latency. It is essential for network administrators to stay up-to-date with these developments in order to maximize the potential of their networks. Additionally, proper cable management practices can help prevent issues such as signal interference or damage to the infrastructure, ensuring smooth operations within a network environment.
In conclusion, while often overlooked compared to flashy hardware or software upgrades, investing in high-quality cables and connectors is essential for maintaining a robust computer network. With continuous innovations in this field, there are always new opportunities to improve network efficiency and reliability through advancements in cable technology.
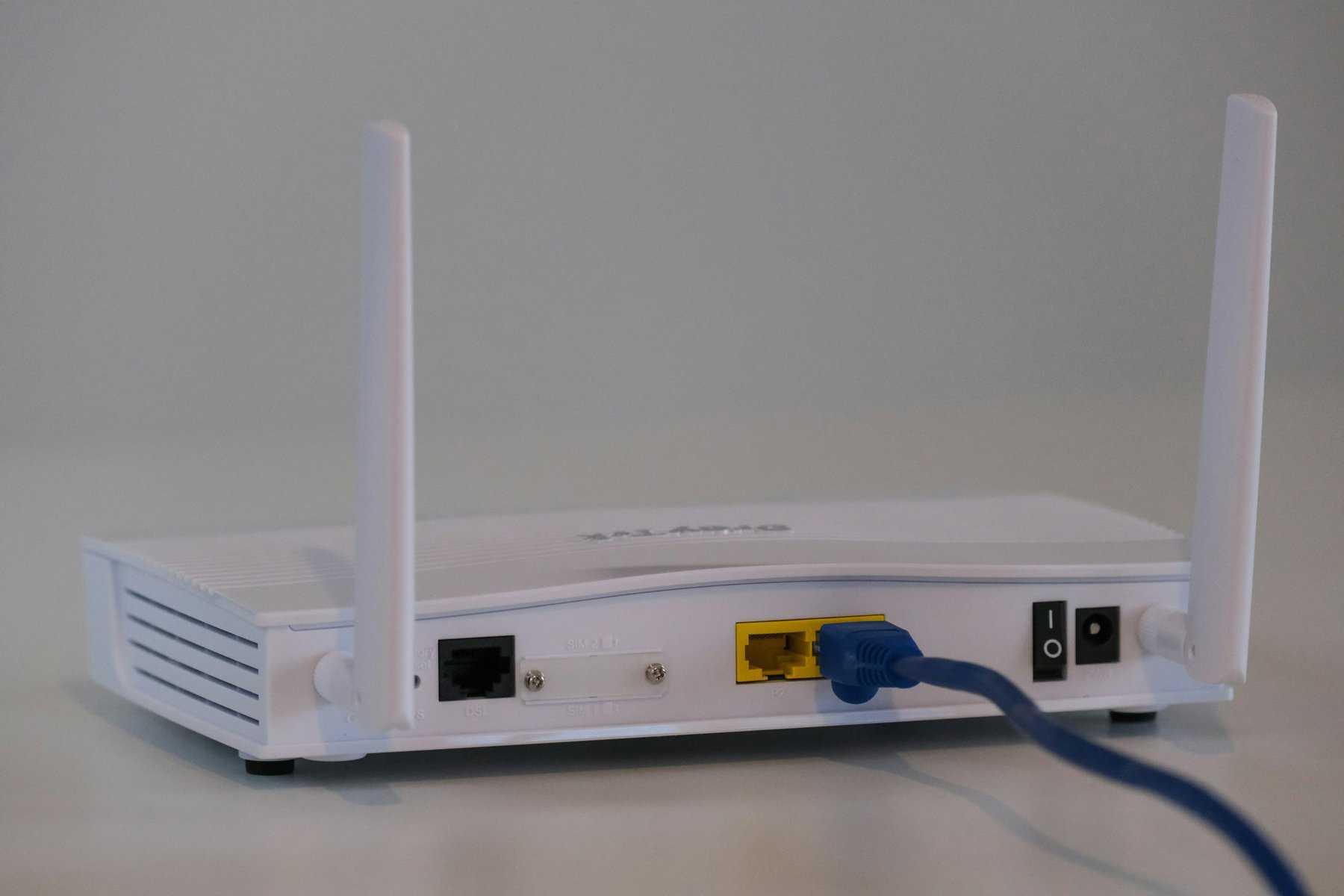


Network devices play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of computer networks. Routers serve as gatekeepers, directing traffic between different networks based on IP addresses. Unlike switches that operate at the data link layer, routers work at the network layer, making intelligent decisions about where to send data packets. Switches, on the other hand, are like traffic directors within a network, efficiently routing data to its intended destination by using MAC addresses.
Hubs may seem similar to switches but lack the intelligence and efficiency of their counterparts. They simply broadcast incoming data packets to all connected devices within a network, leading to potential congestion and inefficiencies. As technology continues to advance, there is a shift towards using more sophisticated routers and switches over hubs for better network performance and security. Understanding the distinct roles of these network devices can help optimize network operations and enhance overall connectivity in an increasingly digital world.
Network Interface Cards (NICs)
Network Interface Cards (NICs) are often overlooked when discussing computer network components, yet they play a crucial role in enabling communication between devices. These hardware components act as the intermediary between the computer and the network, allowing data to be transmitted and received. With advancements in technology, modern NICs can support high-speed connections, multiple protocols, and even wireless connectivity.
One interesting aspect of NICs is their ability to be upgraded or replaced to improve network performance. By installing a higher quality or specialized NIC, users can experience faster data transfer speeds and better reliability. Additionally, some NICs come equipped with features like VLAN support or packet prioritization, which can optimize network traffic management for specific applications or use cases.
In essence, while it may seem like a small component of the overall network infrastructure, choosing the right NIC can have a significant impact on the efficiency and effectiveness of data transmission within a network ecosystem. It's important for users to consider their networking needs and research available NIC options to ensure optimal performance and seamless connectivity.
Servers and Clients: Data sharing devices
Servers and clients play a crucial role in data sharing within computer networks. Servers are powerful devices that store and manage resources, providing services to multiple clients simultaneously. They act as the central hub for data storage, processing requests from client devices such as computers or smartphones.
Clients, on the other hand, are devices that access and utilize resources provided by servers. These devices could be laptops, tablets, or any other device connected to the network seeking information or services. By establishing a connection with servers, clients can access shared data and collaborate with others in real-time. This dynamic exchange of information between servers and clients forms the backbone of efficient data sharing on computer networks.
Data Centers: Centralized network infrastructure
Data centers serve as the heart of modern network infrastructure, providing a centralized hub for storing, processing, and distributing data across a network. These facilities are designed to ensure high levels of security, reliability, and scalability to meet the growing demands of digital services. With an array of servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and cooling systems interconnected in a meticulously planned layout, data centers form the backbone of our increasingly interconnected world.
The evolution of data centers has been marked by advancements in technology that have revolutionized how businesses operate and users access information. From traditional on-premises facilities to cloud-based solutions, data centers continue to adapt to changing trends and requirements. The increasing reliance on data-intensive applications like AI, IoT, and big data analytics underscores the critical role data centers play in supporting innovation and driving digital transformation across various industries.
Wireless Access Points (WAPs) play a crucial role in modern networking environments by enabling wireless devices to connect to a wired network. These devices are like bridges that allow seamless communication between wired and wireless systems, enhancing the flexibility and mobility of users within an organization. By strategically placing WAPs throughout a location, businesses ensure comprehensive coverage and connectivity for all their users, promoting productivity and efficient collaboration.
The evolution of WAP technology has brought about significant advancements in terms of security features, performance capabilities, and management functionalities. Businesses can now deploy sophisticated WAPs that offer seamless roaming functions for users moving between access points without experiencing disruptions in connectivity. Moreover, the integration of advanced encryption protocols and authentication mechanisms within WAPs ensures data privacy and protection against unauthorized access or cyber threats. This emphasis on security highlights the critical role that WAPs play not only in facilitating connectivity but also in safeguarding sensitive information transmitted over wireless networks.
Conclusion: Importance of physical components in networking
In conclusion, it is evident that physical components play a crucial role in the functioning and efficiency of computer networks. While software and virtual technologies have advanced significantly, the foundational hardware elements remain essential for supporting the overall infrastructure. Without reliable cables, routers, switches, and other tangible components, even the most sophisticated software solutions would struggle to deliver connectivity and performance.
Moreover, understanding the importance of physical components in networking emphasizes the need for proper maintenance and investment in high-quality equipment. Neglecting these aspects can lead to network disruptions, slow speeds, security vulnerabilities, and increased downtime. By recognizing the significance of tangible devices in network operations, organizations can make informed decisions when planning and implementing their IT infrastructure to ensure smooth operations and minimize risks associated with hardware failures.